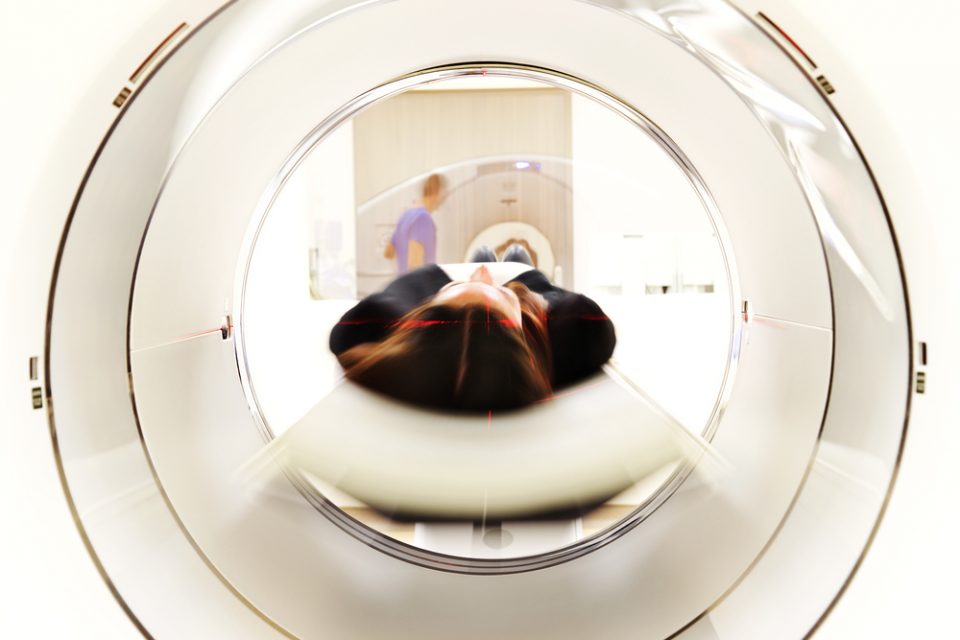
When it comes to back pain, there are many ways spine doctors can determine what ails you, including physical exams, evaluations of your medical history, blood tests or even electromyography.
However, only medical imaging, which includes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans and X-rays, can be used to examine your body’s internal structure to get a deeper understanding of the root cause of your pain or illness.
You may be vaguely familiar with medical imaging, but most people do not know the differences between each type or what they are used for.
Do I Need Imaging for My Back Pain?
It is important to note that imaging is not typically used for treating acute back pain, which lasts for a few days to a few weeks. In fact, a conservative approach is often taken before ordering medical imaging. This may include physical therapy, non-invasive treatment and medication.
Generally, a doctor will only order imaging if symptoms persist beyond six weeks or certain red flags turn up during the physical and medical history evaluation. These red flags include:
- Severe or progressive neurological issues
- Sudden back pain with spinal tenderness
- A serious underlying condition
- Fever
- Trauma
Diagnosing Back Problems With Medical Imaging
Imaging can be used to diagnose a host of mild to severe spinal conditions. Some structural changes or abnormalities, such as herniated discs or tumors, are primarily diagnosed using medical imaging. Since these conditions do not always cause pain, radiographic tests are often the only way to detect them.
Other back problems that can be diagnosed using medical imaging include:
- Osteoporosis
- Arthritis
- Fractured vertebra
- Problems with spine alignment
- Soft tissue problems
- Spinal stenosis
- Degenerative discs
What Is an MRI?
MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves to create a detailed, cross-sectional image of the body’s internal structure. During the procedure, a magnetic field is created in your body and radio waves are sent to the region being examined. This causes the fat and water molecule protons in your bone and tissue to resonate, creating a computer-generated image.
With this image, your doctor can get a clear visual of your bones, joints, ligaments, blood vessels, cartilage and discs. This procedure does not require radiation like X-rays and CT scans often do. It generally takes about 20 to 90 minutes, and it may require intravenous drugs, such as gadolinium-based contrast agents, to provide a clear and accurate diagnostic image.
What Is a CT Scan?
A CT scan, often pronounced as “cat scan,” is similar to an MRI, only it creates a three-dimensional, cross-sectional image using specialized X-ray technology. Contrast dyes and ionizing radiation are often ingested to create a more detailed image.
The machine is essentially a tunnel with a table inside that the patient lays on. A scanner rotates around the patient to create a 360-degree visual. The test is often broken down into “slices” – each slice, or section, is scanned separately for a variety of health conditions.
What Is an X-Ray?
If you have ever been to the dentist or had a broken a bone, you are probably familiar with X-ray testing, which is more commonly used and readily available than the other medical imaging technologies.
X-rays work by sending low levels of electromagnetic radiation through the body to create a 2D image of your skeleton. When the rays hit a dense object, like bone, it appears as a white structure on the image.
However, because only bones are visible with an X-ray, they are used to check for structural issues like osteoporosis, degeneration, fractures and alignment problems. Additional testing using an MRI or CT scan is needed to diagnose soft tissue conditions.
Comprehensive Spine Care in the Dallas-Fort Worth Area
At Spine Works Institute, we understand that back problems are unique to each person. That is why we offer a wide variety of comprehensive spine solutions, including MRI services, so our patients can return to a pain-free lifestyle as quickly and easily as possible.
For more information or to schedule an appointment, call 817.616.0700 or visit us online today.